In-cytoplasm Mitochondrial Transplantation for Stem Cells Engineering & Tissue Regeneration

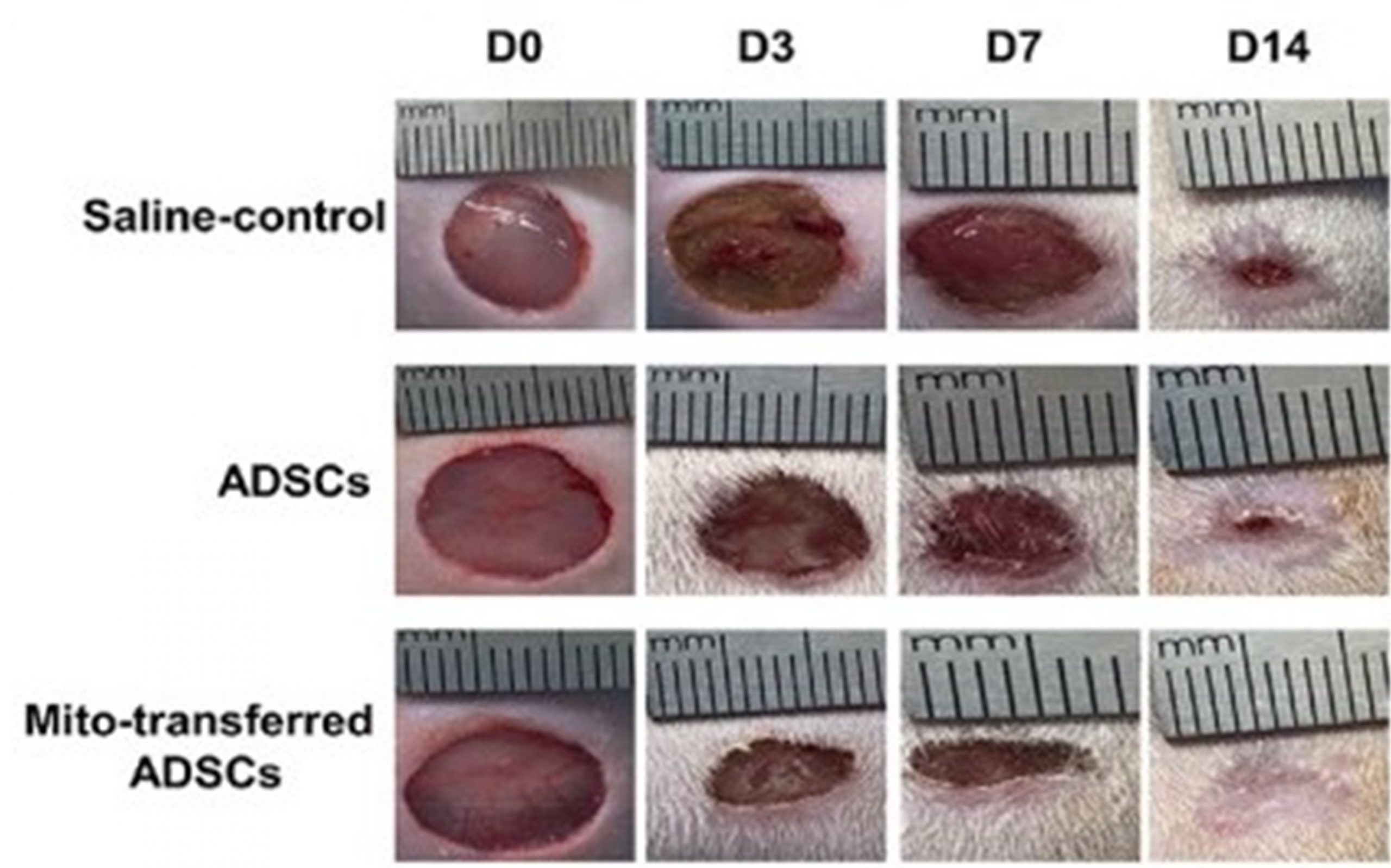
Representative images of the wound area (left) and the corresponding fractions of wounds healed (right) by different treatments.
News Release, Skin Aging & Challenges – August 31, 2022
Stem cell therapies are unsatisfactory due to poor cell survival and engraftment. Stem cells used for therapy must be properly “tuned” for a harsh in vivo environment.
Ouyang et al. reported that the transfer of exogenous mitochondria (mito) to adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ADSCs) can effectively boost their energy levels, enabling efficient cell engraftment. The entire process of exogenous mitochondrial endocytosis was captured by high-content live-cell imaging.
Mitochondrial transfer lead to acutely enhanced bioenergetics, with nearly 17% of higher adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) levels in ADSCs treated with high mitochondrial dosage and further resulted in altered secretome profiles of ADSCs. It also induced the expression of 334 mRNAs in ADSCs, which are mainly linked to signaling pathways associated with DNA replication and cell division.
They hypothesize that increase in ATP and cyclin-dependent kinase 1 and 2 expression might be responsible for promoting enhanced proliferation, migration, and differentiation of ADSCs in vitro. More importantly, mito-transferred ADSCs display prolonged cell survival, engraftment and horizontal transfer of exogenous mitochondria to surrounding cells in a full-thickness skin defect rat model with improved skin repair compared with nontreated ADSCs.
These results demonstrate that intracellular mitochondrial transplantation is a promising strategy to engineer stem cells for tissue regeneration.
© Photo Copyright: Ouyang et al.
Join Dr. Ouyang in Skin Ageing & Challenges 2022 this November to know more about the in-cytoplasm mitochondrial transplantation procedure.
Skin Ageing & Challenges 2022
November 17-18, 2022 – Lisbon, Portugal
www.skin-challenges.com
